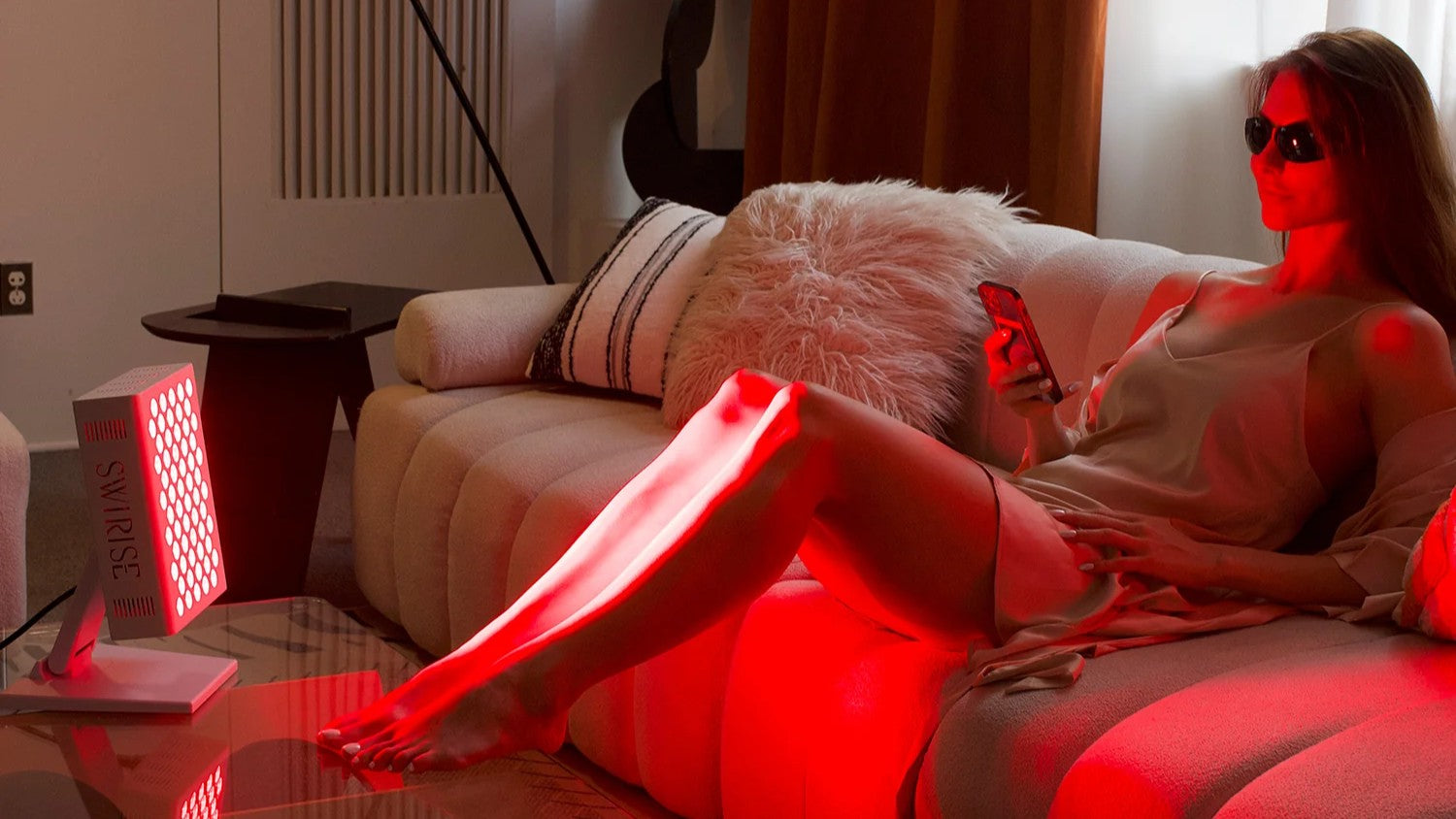
How Irradiance Impacts Red Light Therapy Results
JustinLinIn recent years, red light therapy has gained significant attention due to its potential health benefits. From accelerating wound healing to reducing pain, light therapy is becoming an increasingly popular alternative treatment. However, one crucial factor that influences the effectiveness of light therapy is irradiance,the intensity of light hitting a specific area.
In this blog post, we'll explore what irradiance means in the context of light therapy, its effects on treatment outcomes, and how it influences the healing process.
What is Irradiance in Light Therapy?
Irradiance refers to the amount of light energy received per unit area, measured in watts per square meter (W/m²) or milliwatts per square centimeter (mW/cm²). It is a key parameter in light therapy, as it directly affects how much light energy is absorbed by tissues, which in turn determines how effective the treatment is. In simple terms, irradiance is a measure of how intense the light source is.
Formula for Irradiance:
I=P/A
Where:
- I = irradiance (W/m² or mW/cm²)
- P = power of the light source (W)
- A = area the light covers (cm² or m²)
Understanding this formula is crucial for determining the optimal irradiance needed for specific treatments
To Unlock the secrets to optimal red light therapy doses for maximum benefits, check out our Red Light Therapy Dosing Guide.
How Irradiance Affects Treatment Outcomes
Irradiance plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of light therapy. The level of irradiance required depends on several factors, such as the treatment target (e.g., skin conditions, wound healing, or pain relief) and the type of light therapy being used.
1. Low Irradiance
Typically used for long-term healing, inflammation reduction, and skin repair. Red light therapy, for instance, uses low irradiance to stimulate cellular metabolism, increase blood circulation, and accelerate tissue regeneration. Lower irradiance levels also activate mitochondrial pigments to boost ATP production, helping repair skin and soft tissues.
2. High Irradiance
Used when faster treatment effects are desired. For instance, high irradiance can be beneficial when treating deeper tissues or acute pain. However, too high an irradiance may lead to thermal effects, skin burns, or tissue damage, so careful regulation is necessary.
3. Treatment Time and Irradiance
There is an important relationship between irradiance and treatment time in light therapy. A lower irradiance typically requires a longer treatment duration to achieve the same therapeutic effect. Conversely, higher irradiance levels usually produce the same effect in a shorter amount of time.
Irradiance and Different Light Therapy Devices
Different light therapy devices require different irradiance settings, depending on their design and intended use. Let's explore a few common types of devices and how irradiance plays a role:
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
These devices typically use low irradiance (e.g., 5–100 mW/cm²) and work by delivering low-power laser light to promote cell repair, reduce pain, and decrease inflammation. LLLT is often used for conditions like arthritis and wound healing.
- UV therapy
UV therapy, commonly used to treat skin conditions like psoriasis, requires higher irradiance levels to deliver therapeutic benefits. However, careful control is necessary to prevent overexposure, which could damage the skin.
- LED Light Therapy:
LED light devices are commonly used for surface-level treatments, such as skincare and tissue regeneration. These devices may operate at lower irradiance levels but require longer treatment times to produce significant effects.
Wavelength and Irradiance in Light Therapy
In addition to irradiance, wavelength plays a crucial role in light therapy. While irradiance determines the intensity of light energy, wavelength affects how deeply light penetrates the skin and tissues, influencing which tissues can benefit from therapy. Together, both factors—irradiance and wavelength—determine the effectiveness of light therapy and its suitability for different therapeutic goals.
- Red Light (600–700 nm): This wavelength is effective for treating superficial skin layers, promoting healing, reducing pain, and improving skin appearance.
- Near-Infrared Light (700–1100 nm): This wavelength penetrates deeper tissues, making it ideal for muscle, joint, and bone therapy.
For instance, near-infrared therapy often uses higher irradiance levels (100–200 mW/cm²) to treat deeper layers of the body, whereas red light therapy typically operates at lower irradiance levels (around 20–50 mW/cm²) to avoid excess heat buildup that could harm the skin.
To learn more about how different wavelengths affect the skin and deeper tissues, check out our Red Light Wavelength: A Complete Guide.
How Red Light Therapy Benefits from Irradiance Control
The benefits of red light therapy are closely tied to controlling the irradiance and wavelength used during treatment:
- Pain Relief: Red light therapy is effective in managing chronic pain, thanks to its ability to stimulate cellular repair and increase circulation at lower irradiance levels.
- Skin Rejuvenation: For skin healing and anti-aging treatments, red light at lower irradiance (20–50 mW/cm²) enhances collagen production, reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: By promoting cellular regeneration, low irradiance red light therapy speeds up tissue repair for both acute and chronic wounds.
These benefits underscore the importance of understanding irradiance and how it impacts the efficacy of red light therapy and other light-based treatments.
Conclusion: Mastering Irradiance for Optimal Light Therapy
In light therapy, irradiance is one of the most important factors influencing treatment outcomes. By choosing the correct irradiance levels for different therapeutic needs, practitioners can optimize healing and ensure effective, safe treatments. Whether you’re looking to alleviate pain, rejuvenate skin, or promote faster healing, understanding and adjusting irradiance is crucial to achieving the best possible results with light therapy.